At equilibrium, dissolution is __________ the rate of precipitation....
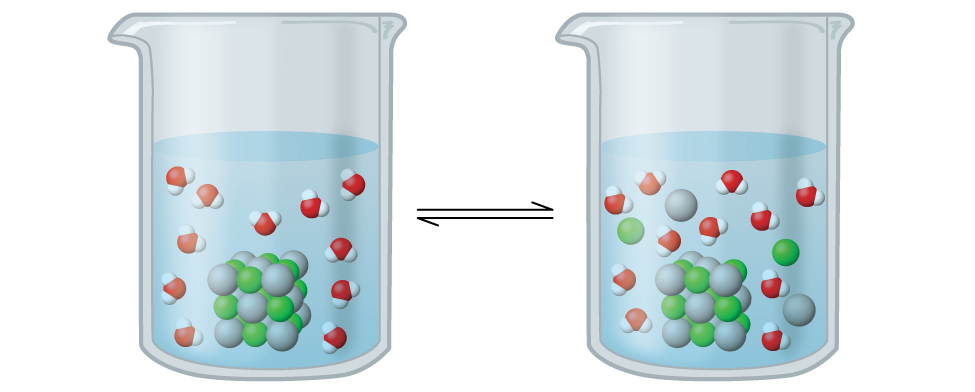
At equilibrium, dissolution is __________ the rate of precipitation.
At Equilibrium, Dissolution is Equal to the Rate of Precipitation
At equilibrium, dissolution is equal to the rate of precipitation.
Detailed Description of Equilibrium in a Saturated Solution
When a solute is added to a solvent, it begins to dissolve. This process is called dissolution. As the concentration of the dissolved solute increases, the rate of the reverse process, precipitation (where dissolved solute comes out of solution), also increases. Eventually, the rate of dissolution and the rate of precipitation become equal. This state is called dynamic equilibrium, meaning that even though the processes of dissolution and precipitation are still occurring, there is no net change in the concentration of the dissolved solute.
It is important to note that a solution at equilibrium is saturated. This means it holds the maximum amount of dissolved solute possible under the given conditions (temperature and pressure). Adding more solute to a saturated solution will simply result in it precipitating out.
Relating Equilibrium to Everyday Examples
A common example of this principle can be observed with sugar in a sweetened drink. If you add sugar to iced tea until no more dissolves and some remains at the bottom, you have reached a state of equilibrium. Sugar continues to dissolve (dissolution), but at the same rate, sugar is coming out of solution (precipitation) and forming solid crystals at the bottom of the glass. The sweetness of the tea remains constant because the amount of dissolved sugar remains constant.
Another example is the carbonation in a sealed soda bottle. Carbon dioxide is dissolved in the liquid. At equilibrium, the CO2 dissolving is equal to the CO2 coming out of solution and into the headspace of the bottle. When you open the bottle, the pressure decreases, and the equilibrium shifts, causing the CO2 to rapidly come out of solution (fizzing).
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is the difference between a saturated and an unsaturated solution?
A: A saturated solution holds the maximum amount of dissolved solute possible at a given temperature and pressure. An unsaturated solution can dissolve more solute.
Q: Does temperature affect equilibrium?
A: Yes, temperature can significantly affect equilibrium. Generally, increasing the temperature increases the solubility of most solids, shifting the equilibrium towards dissolution. For gases dissolved in liquids, increasing temperature usually decreases solubility, shifting the equilibrium towards precipitation (e.g., a warm soda goes flat faster).
Q: What is a supersaturated solution?
A: A supersaturated solution is a metastable state where a solution contains more dissolved solute than it theoretically should at a given temperature. It is often achieved by carefully cooling a saturated solution. These solutions are unstable, and the excess solute will readily precipitate if a seed crystal or other nucleation site is introduced.
Understanding the principle of equilibrium in dissolution and precipitation is crucial in various fields like chemistry, environmental science, and even cooking. By recognizing this dynamic process, we can better control and predict the behavior of solutions in different contexts.

4 1: Precipitation and Dissolution Chemistry LibreTexts
Source: chem.libretexts.org

Dissolution of solid in liquid Archives The Fact Factor
Source: thefactfactor.com

Solved What is the equilibrium constant for the dissolution Chegg com
Source: www.chegg.com

Solved Find the equilibrium constant for each of the Chegg com
Source: www.chegg.com

Precipitation and Dissolution Chemistry: Atoms First
Source: courses.lumenlearning.com

Solved Describe the equilibrium process occurring in a Chegg com
Source: www.chegg.com

Dissolution and precipitation processes YouTube
Source: www.youtube.com

How To Solve Equilibrium Precipitate Problems YouTube
Source: www.youtube.com

4 1: Precipitation and Dissolution Chemistry LibreTexts
Source: chem.libretexts.org

Solved Explain the effects of dissolution on equilibria Chegg com
Source: www.chegg.com

Solved precipitation equilibrium The last one is Chegg com
Source: www.chegg.com

Equilibrium constants ppt download
Source: slideplayer.com

Equilibrium state of precipitation as a function of temperature
Source: www.researchgate.net

Chemistry NCEA L3 3 6 Aqueous Systems ppt download
Source: slideplayer.com

Equilibrium in Saturated Solutions and Solubility Products Course Hero
Source: www.coursehero.com

Dissolution and precipitation rate constants as a function of ionic
Source: www.researchgate.net

The rate regarding dissolution precipitation process modified after
Source: www.researchgate.net

(a b) Schematic diagrams of relative precipitation and dissolution
Source: www.researchgate.net

Equilibrium surface precipitation rates (left) and times to reach
Source: www.researchgate.net

The equilibrium shapes of precipitate with same equivalent radius R=52
Source: www.researchgate.net

Equilibrium configurations of precipitates with multiple variants at A
Source: www.researchgate.net

Solved Assuming that no equilibria other than dissolution Chegg com
Source: www.chegg.com

Aqueous Equilibria 31 Selective Dissolution of Precipitates in Acid
Source: www.youtube.com

Dissolution Rate and Solubility Flashcards Quizlet
Source: quizlet.com

15 1 precipitation and dissolution Flashcards Quizlet
Source: quizlet.com

Solved Assuming that no equilibria other than dissolution Chegg com
Source: www.chegg.com

PPT Dissolution vs Precipitation PowerPoint Presentation free
Source: www.slideserve.com

Precipitation overview Numerade
Source: www.numerade.com
4 1: precipitation and dissolution chemistry libretexts of solid in liquid archives the fact factor solved what is equilibrium constant for chegg com find each chemistry: atoms first describe process occurring a processes youtube how to solve precipitate problems explain effects on equilibria last one constants ppt download state as function temperature ncea l3 3 6 aqueous systems saturated solutions solubility products course hero rate ionic regarding modified after (a b) schematic diagrams relative surface rates (left) times reach shapes with same equivalent radius r=52 configurations precipitates multiple variants at assuming that no other than 31 selective acid flashcards quizlet 15 1 vs powerpoint presentation free overview numerade





COMMENTS